Fintech: Overview of the IT payment industry

Introduction to Fintech

FinTech (Financial Technology) - FinTech is an area that is developing and attracting more attention each year. As an industry, FinTech includes various companies that use IT technologies to offer financial products and services. This diversity ranges from mobile payments and digital currencies to investment platforms and more.
Today's FinTech encompasses much more than just mobile payments or banking. It includes the development of artificial intelligence and machine learning, blockchain technologies, and even augmented and virtual reality in the financial sector.
The FinTech philosophy places the consumer at the center. FinTech companies strive to offer more convenient, faster, and personalized services to meet the needs and expectations of the modern consumer. It is a world where convenience, transparency, and individuality are valued above all.
However, like any industry in its early stages of development, FinTech faces its problems and challenges, ranging from regulatory issues to data security concerns.
For beginners, I recommend reading an article by Stripe, where they explain the main terms of the FinTech industry.
Difference Between FinTech and Banking
One of the most common questions people have is, "What is the difference between FinTech and banking?"
Let's look at the differences between the classic banking systems and FinTech:
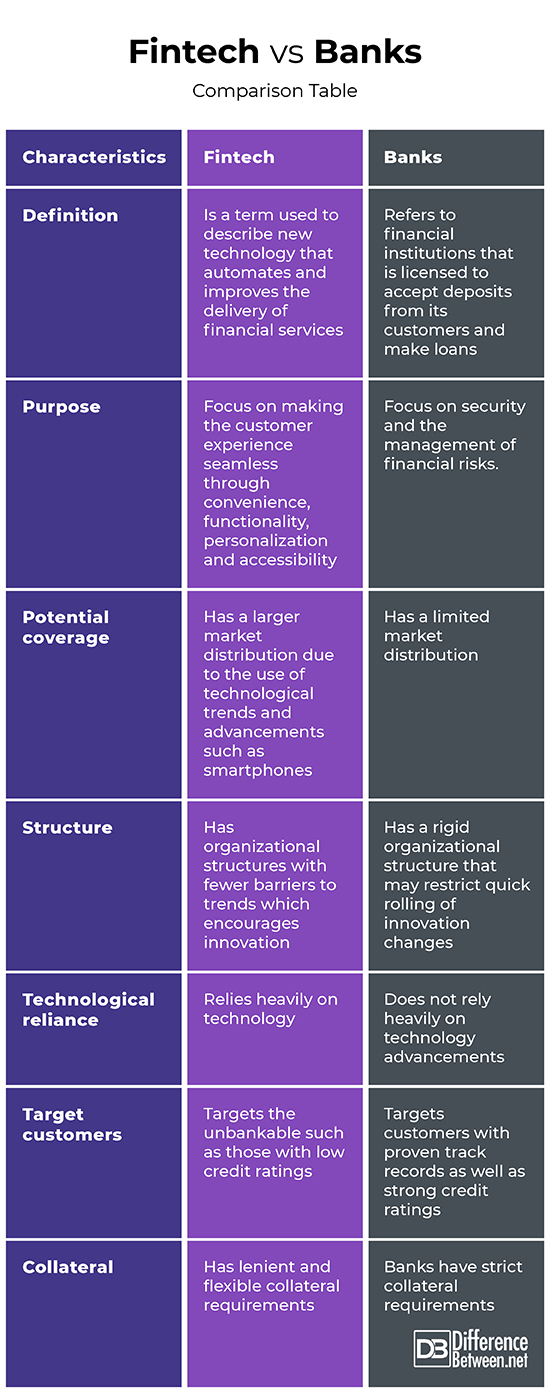
Banks are such conservative grandparents who keep everything reliable, clear, and orderly, and fintech is your younger brother, with a spinner, youth slang, and new trends.
Glossary of Terms in FinTech
- Blockchain: A distributed ledger technology that ensures the security, transparency, and immutability of financial transactions.
- Cryptocurrency: Digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security and control over the creation of new units.
- P2P Lending (Peer-to-Peer Lending): Platforms that allow users to lend and borrow money directly without the intermediation of traditional financial institutions.
- Digital Wallets: Applications that store payment data and cryptocurrencies for quick and convenient online transactions.
- Tokenization: The process of converting rights to an asset into a digital form that can be recorded on a blockchain and easily transferred.
- Open Banking: An approach that allows third parties to access banking data through APIs to create new applications and services.
- Satellite Currency: A concept related to using satellite technologies to manage and process digital currencies and payments, providing enhanced security and independence from traditional banking systems.
- Bank Issuer: A bank or financial institution that issues credit cards or other payment instruments to clients and is responsible for processing transactions.
- Bank Acquirer: A bank that processes credit and debit card transactions on behalf of a merchant, accepting payments from card issuers and transferring them to merchants.
- Neobanks: Fully digital banks that do not have physical branches and offer fast, convenient, and often cheaper banking services.
- Smart Contracts: Software algorithms in blockchain networks designed to automatically execute, control, or document legally significant events and actions according to contract terms.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Blockchain-based financial services that operate without traditional central financial intermediaries.
- Payment Gateway: A service that authorizes and processes payments for online stores and businesses.
- API Banking: Allows third parties to develop financial services and access banking functionalities through their APIs.
- Algorithmic Trading: The use of algorithms to automate trading strategies and execute large volumes of orders in financial markets.
- Factoring: A financial service where a business sells its accounts receivable (e.g., invoices) to a third party (the factor) to accelerate cash flow.
- Peer-to-Peer Payments (P2P Payments): Electronic money transfers made directly between individuals through specialized platforms.
- Credit Scoring: The use of algorithms and statistical models to assess a customer's creditworthiness and the likelihood of loan repayment.
- Digital Identification: Technologies and systems that enable the verification of a user's identity in the digital space for access to financial services.
- Microfinancing: Providing financial services and small loans to small businesses and individuals who typically do not have access to traditional banking credit.
- Digital Assets: Any assets existing in digital form, including cryptocurrencies, tokens, digital shares, and other rights to digital goods or services.
- Financial Monitoring: Systems and tools for tracking and analyzing financial transactions, often used to prevent fraud and money laundering.
- Quantitative Finance: The application of mathematical models and big data to analyze financial markets and create trading strategies.
- Cardholder: An individual or organization that has been issued a debit or credit card and is authorized to use it.
- Merchant: A business or individual that accepts payments for goods or services. In the context of e-commerce, this typically refers to websites or retail sellers.
- Payment Processor: A company that processes debit and credit card transactions on behalf of merchants and banks.
- Merchant Account: A type of bank account that allows a business to accept and process electronic card payments.
- Chargeback: The process of returning money to a buyer at the expense of the seller in the case of a disputed or fraudulent transaction.
- EMV (Europay, MasterCard, and Visa): A global standard for credit and debit cards with chips to ensure transaction security.
- NFC (Near Field Communication): A short-range wireless communication technology used for data exchange between devices, such as for contactless payments.
- KYC (Know Your Customer): The process used by companies to verify the identity of their clients in compliance with anti-money laundering laws.
- AML (Anti-Money Laundering): A set of procedures, laws, and regulations designed to prevent money laundering through financial systems.
Basic technologies and tools in Fintech
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies
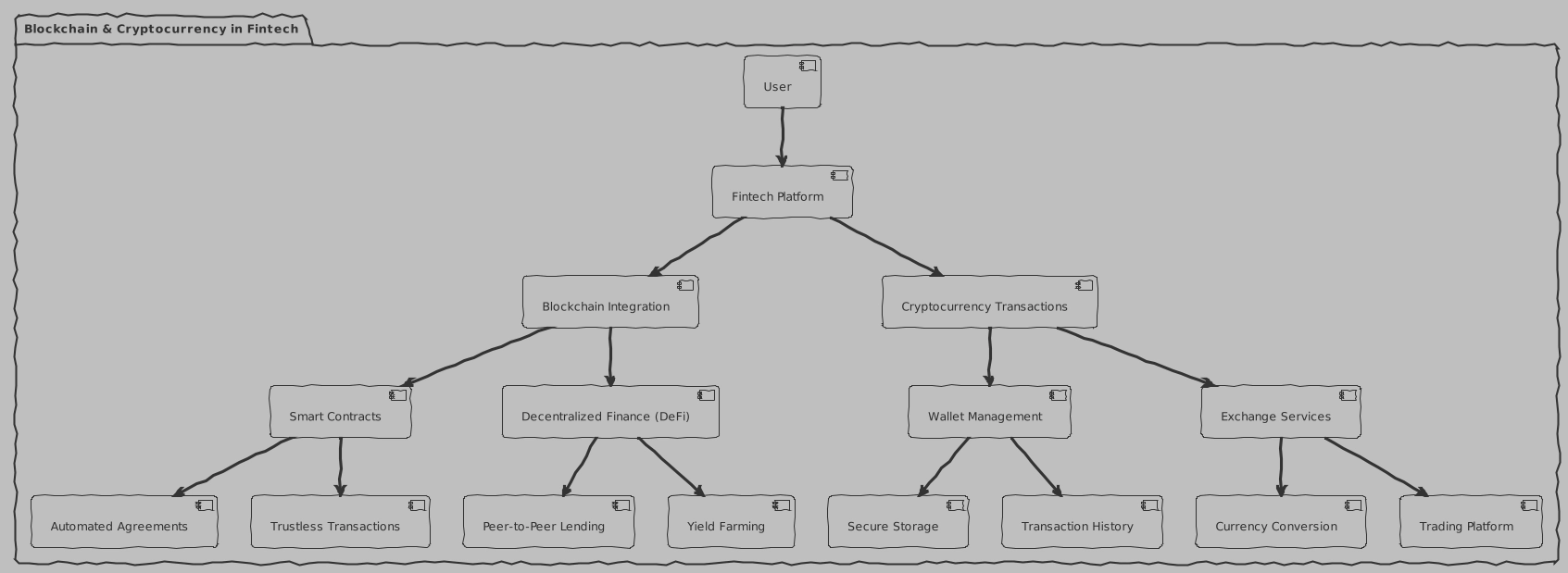
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies have changed the understanding of financial transactions. The idea of decentralized transactions, embodied by cryptocurrencies, is essentially a game changer in the financial industry. And although many banks are still wary of these innovations, some are already actively experimenting with the use of blockchain technology for their needs.
Let's look at each sub-item from the diagram in a little more detail:
Blockchain Integration
Blockchain integration in fintech opens up new opportunities for transparency and security of financial transactions. Let's figure out how it works:
Smart Contracts
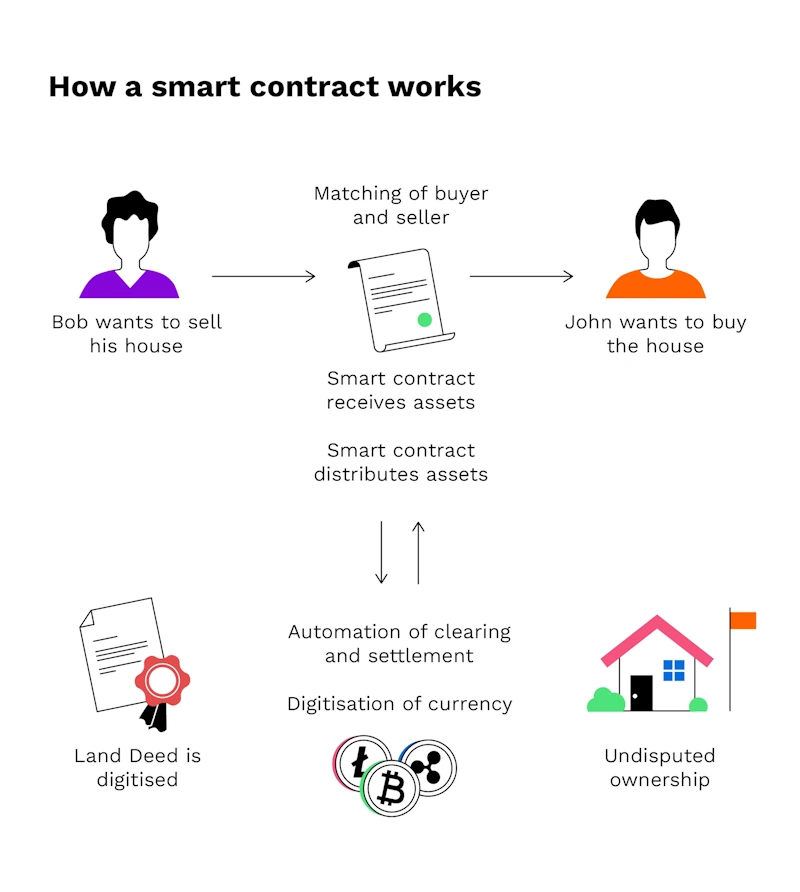
Smart contracts are tools that automatically fulfill the terms of a contract when certain conditions occur. They are important for:
- Automated Agreements – Automating agreements simplifies the process of entering into and executing contracts, minimizing human errors and ensuring compliance with terms
- Trustless Transactions – Thanks to smart contracts, you can conduct secure transactions without having to trust the other party.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
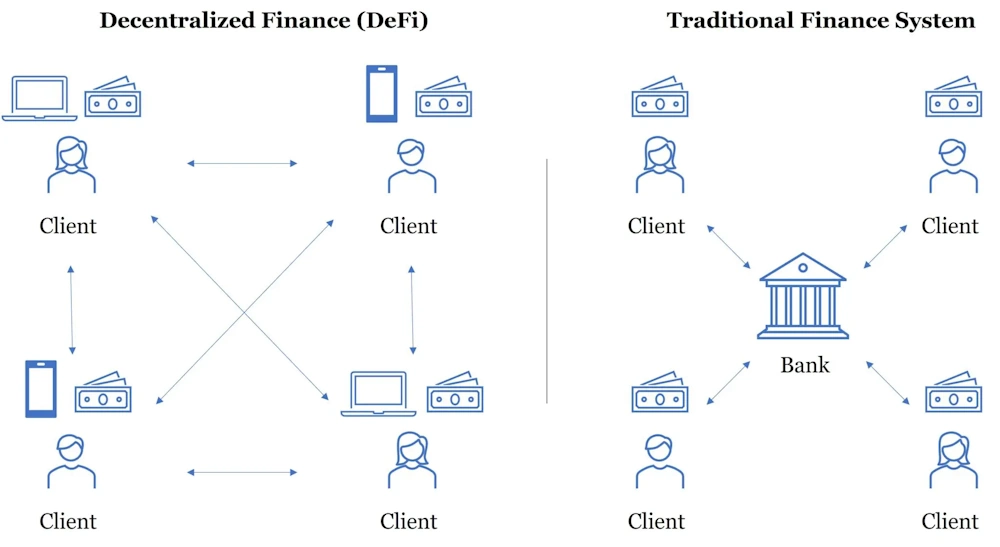
Decentralized finance or DeFi uses blockchain to create open and accessible financial systems. In this category:
- Peer-to-peer lending – P2P lending allows users to borrow and lend money to each other directly, without intermediaries.
- Yield Farming is a way to generate income from cryptocurrency assets based on investing in various DeFi protocols.
Cryptocurrency Transactions
Cryptocurrency transactions include:
Wallet Management
Wallet management includes several aspects:
- Secure Storage – secure storage of cryptocurrencies is important to protect assets from hacking.
- Transaction History – transaction history provides complete transparency of all transactions in the wallet.
Exchange Services
Cryptocurrency exchange services allow users to buy, sell, and exchange cryptocurrencies. These services include:
- Currency Conversion – Currency conversion makes it easier to switch between different cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies.
- Trading Platform – Trading platforms provide the user with an interface for actively trading and investing in cryptocurrencies.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Let's consider the points in more detail:
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly important in FinTech, and here's why:
Personalization
Personalization uses AI to create an individual experience for each user. This includes:
- Recommendation Systems: Analyze past user behavior to suggest products or services that may interest them.
- User Behavior Analysis: Helps understand what exactly the client is looking for and offers appropriate solutions.
Automation
Automation speeds up and optimizes processes such as:
- Automatic Decision Making: Systems can automatically make decisions based on predefined rules and algorithms.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Allows the automation of routine and repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more complex tasks.
Fraud Detection
Fraud detection systems use AI to identify suspicious activities:
- Anomaly Detection: Involves monitoring transactions and activities to identify unusual patterns.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Allows immediate response to potential threats.
Machine learning
Forecasting
Forecasting uses historical data to predict future events, such as stock prices or market trends.
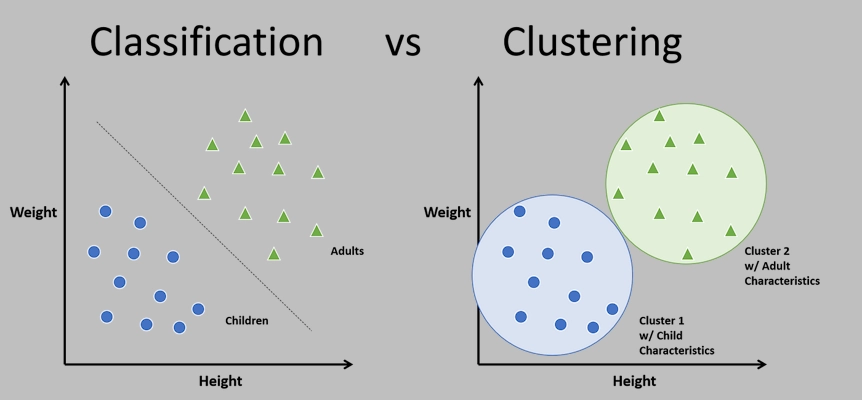
Clustering
Clustering group data based on similarities helps to understand the structure and relationships in the data.
Classification
Classification is used to automatically separate data into different categories, for example, to determine a customer's creditworthiness.
Overall, the use of AI and machine learning in fintech allows for more efficient, secure, and personalized solutions, which ultimately enriches the user experience and increases conversions for businesses.
API (Application Programming Interfaces)
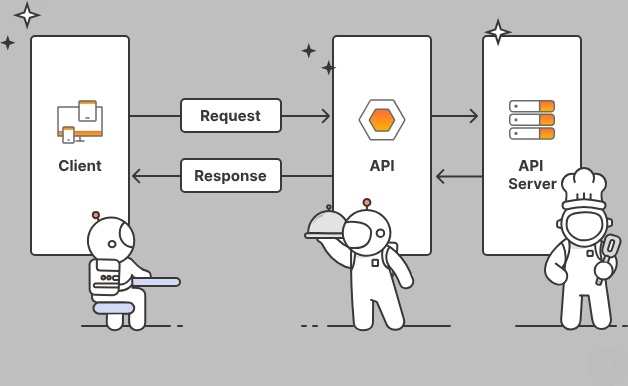
APIs are a set of instructions that allow different programs and applications to communicate with each other. In fintech, APIs play a key role in integration with acquiring and issuer banks. This allows you to create flexible and reliable platforms for conducting transactions, as well as integrate various external services and functions into existing systems.
Mobile payment platforms

Mobile payments are becoming increasingly important in today's world. They offer the convenience and speed that today's consumers demand. This has led to the development of a range of technologies related to mobile payments, including contactless payments, mobile wallets and P2P payments.
Cloud technologies

Cloud technologies have played a huge role in the development of fintech, providing companies with flexible and scalable infrastructure. They enable fintech companies to easily scale their operations, process large volumes of data, and provide high-quality services to clients around the world.
Key players and products in Fintech

Ссылаясь на этот рейтинг рассмотрим топ компании в fintech индустрии и их ключевые продукты:
Referring to follow rating, let's look at the top companies in the fintech industry and their key products:
1. Visa
- VisaNet: A global payment processing network that processes over 65,000 transactions per second.
- Visa Checkout: Online payment solution to simplify online shopping.
2. Mastercard
- Mastercard Payment Gateway: Online payment processing solution that integrates with various payment methods.
- Masterpass: Secure digital wallet for online payments.
3. Tencent
- WeChat Pay: A mobile payment service that allows users to easily make payments via WeChat. Popular in the Chinese market.
- QQ Wallet: Another wallet from Tencent, integrated with the popular QQ messenger.
4. Ant Financial
- Alipay: One of the largest mobile payment services in China.
- Yu'e Bao: Platform for investing in money funds.
5. Coinbase
- Coinbase Wallet: Platform for buying, selling, and storing cryptocurrencies.
- Coinbase Commerce: A solution for accepting cryptocurrency payments in business.
6. PayPal
- PayPal Wallet: Online wallet for payments and money transfers.
- Venmo: A service for friends and family that allows you to quickly send and receive money.
7. Fiserv
- Clover POS System: Payment processing solution for retail businesses.
- Popmoney: Service for transferring money between individual users.
8. Stripe
- Stripe Payments: Online payment platform for business.
- Stripe Billing: Solution for managing subscriptions and recurring payments.
9. Adyen
- Adyen Payments Platform: Global payment processing platform.
10. Nubank
- Nubank Digital Account: Digital bank account with free services.
- Nubank Credit Card: No-annual credit card with app management.
11. Checkout.com
- Payments processing: Online payment processing solution.
12. Square
- Square Point of Sale: Payment system for retail business.
- Cash App: Payment system for retail business.
13. Revolut
- Revolut App: Mobile bank with investing, currency exchange, and much more.
Features of domain development in Fintech

High safety requirements
When working with users' finances and personal data, security is a top priority. Fintech developers must take measures to ensure data security, including using the latest encryption methods, two-factor authentication, biometrics, and other security methods. Regular penetration testing and ongoing security training are also important.
Regulatory Compliance
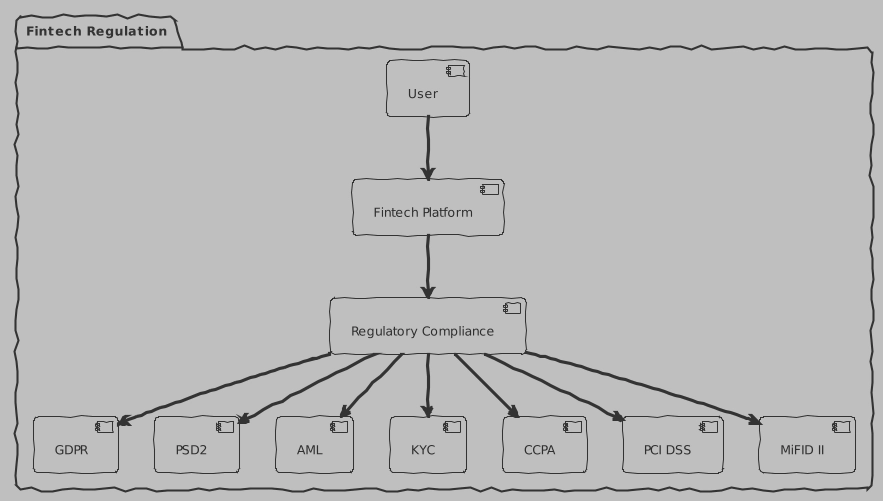
Fintechs are subject to strict regulatory requirements in every country where they operate. Here are the main regulations that the fintech industry faces:
GDPR
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): This is a European Union regulatory requirement that came into force in May 2018. The GDPR provides data protection and privacy for all individual citizens of the European Union and the European Economic Area. It also regulates the export of personal data outside the EU and EEA.
PSD2
PSD2 (Payment Services Directive 2): This is a European Union directive that regulates payment services and payment providers throughout the EU and EEA. It includes security requirements for initiating and processing electronic payments, as well as protecting consumer data.
AML
AML (Anti-Money Laundering): These are international requirements that require financial institutions to take measures to prevent and detect attempts at money laundering.
KYC
KYC (Know Your Customer): This is the process that financial companies and institutions must go through to confirm the identification of their clients. This is part of a broader approach to preventing money laundering and terrorist financing.
CCPA
CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): This is a California law that gives consumers broad rights regarding their personal information, including the right to know what personal information is being collected, sold, or disclosed and to whom, and the right to stop the sale of their personal information.
PCI DSS
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): This is an international security standard that sets requirements for all companies that process, store, or transmit credit card information.
MiFID II
MiFID II (Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II): This is EU legislation that regulates firms providing services related to financial instruments such as shares, bonds, units of investment funds, and derivatives, and the places where these instruments are traded.
Integration with other systems
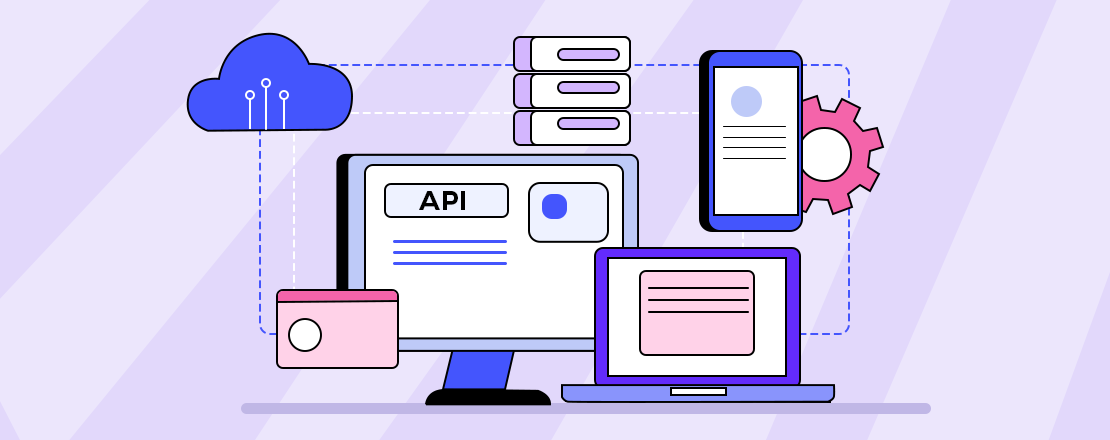
Fintech products often need to integrate with existing banking systems, payment systems, external APIs, and other services. This requires a deep understanding and ability to work with a variety of technologies and protocols.
Scalability Requirements

С возрастающим объемом транзакций финтех приложения должны быть готовы к масштабированию. Это означает, что архитектура приложения должна быть спроектирована таким образом, чтобы она могла эффективно масштабироваться и обрабатывать возрастающую нагрузку. Но следует помнить и об оптимизации на уровне приложения. Ведь сделанная ошибка к примеру которая нагружает CPU умноженная на 1000 или 10 000 одновременных запросов делает больно серверу. Более подробно вопросы матабирования разбираем в этой статье
With increasing transaction volumes, fintech applications must be ready to scale. This means that the application architecture must be designed in such a way that it can scale efficiently and handle increasing workload. But you should also remember about optimization at the application level. After all, a mistake made, for example, that loads the CPU multiplied by 1000 or 10,000 simultaneous requests hurts the server. More for scaling you can read here.
Usability

Any application must be convenient for the end user. This includes ease of use, adaptive design, fast loading, and responsiveness. UX/UI designers play a crucial role in creating products that people will want to use.
All these features make development in the FinTech domain a challenging but interesting task. This field is constantly evolving, and developers need continuous learning and adaptation to new technologies and trends.
Trends and future
So, let's go through the trends and future of the fintech industry. What lies ahead?
Personalization and AI

Personalization has already become a key element of fintech products, and this will increase in the future. AI and machine learning help with this by analyzing user data and offering personalized products, services or recommendations.
Open Banking
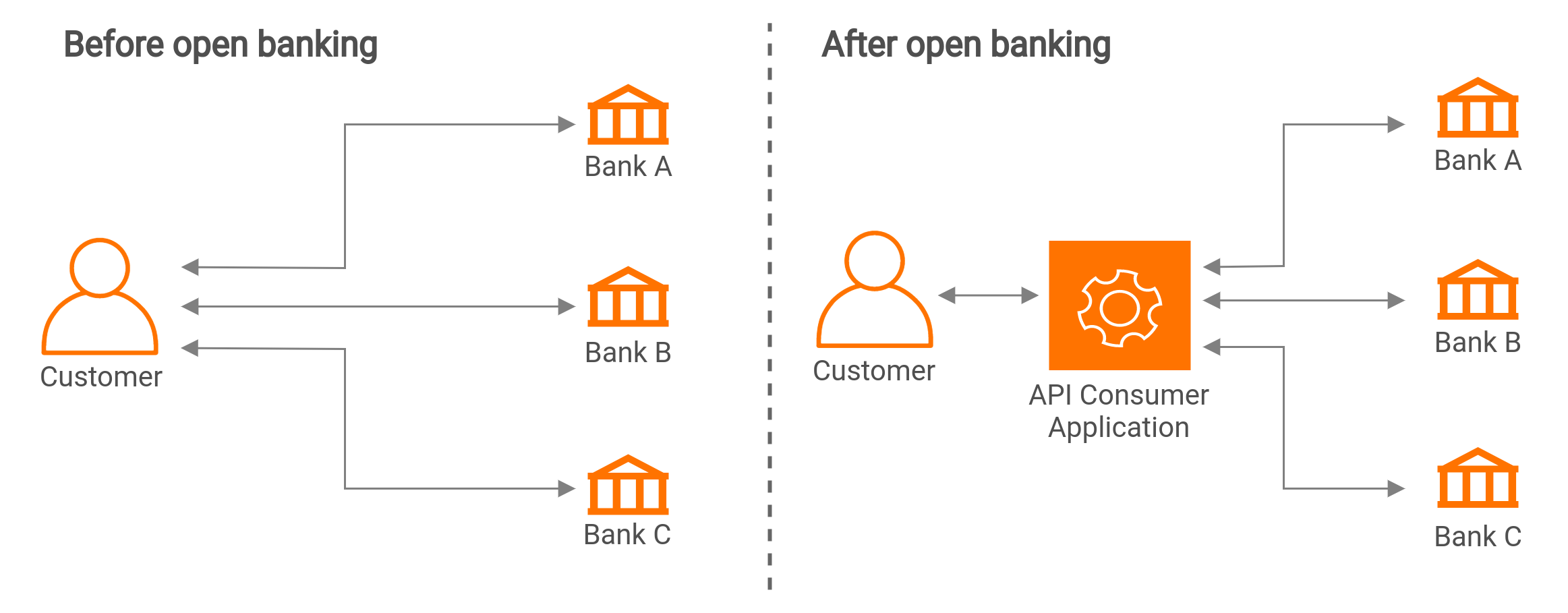
Open Banking, or open banking services, is becoming increasingly popular. With the help of banking system APIs, companies can provide customers with better services, access to account information, the ability to make payments, etc.
Блокчейн и DeFi

Blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi) continue to gain momentum. Users increasingly value the transparency, security, and efficiency that these technologies provide. The emergence of products such as stable coins, decentralized exchanges (DEX), and lending platforms is changing the industry.
Neobanks

Neobanks, or digital banks, continue to expand their presence. They offer the user convenient and innovative financial services, bypassing traditional banking structures.
Regulatory Technologies (RegTech)
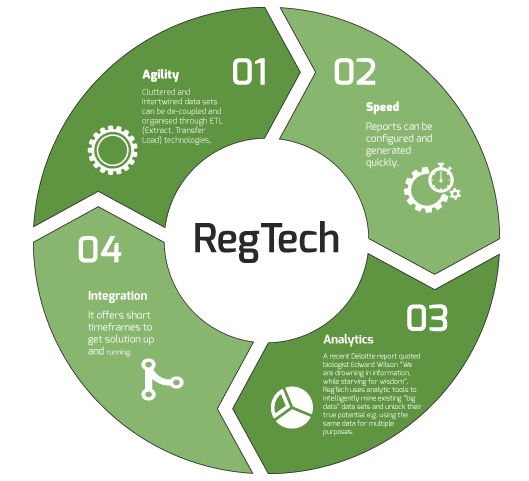
With increasing regulatory pressure and safety requirements, companies are increasingly investing in regulatory technology. These technologies help simplify and automate risk management, compliance, and reporting processes.
Cybersecurity

Cybersecurity will remain at the forefront as threats become more complex and sophisticated. New technologies and approaches to information security will emerge to protect users' financial data.
At the same time, the fintech field remains open to innovation. Changing consumer needs, new technologies, and regulations will lead to the emergence of new products and services. There is always room in this field for those who are willing to innovate and think outside the box.
Conclusion

The fintech domain continues to evolve rapidly in response to changing consumer demands and continuous technological innovation. Blockchain, AI, machine learning, open banking and other technologies are redefining the way we transact financially and offering new opportunities for consumers and businesses.
On the other hand, increasing regulation and growing safety requirements are increasing the complexity in this area. Advances in cybersecurity and regulatory technology will play a key role in protecting the interests of consumers and businesses.
Overall, fintech is an exciting and dynamic field where new ideas and approaches are constantly emerging. In the future, we can expect to see even more innovative products and services that will make our financial lives even more convenient and efficient.